Test Automation Statistics for Making the Right Decisions
Explore reliable and useful test automation statistics to learn more about current trends, including testing challenges, testing processes, and testing tools.

In today’s fast-changing world, companies have to look both inward and outward for improvements in their software quality practices. Let’s check the pulse of test automation by taking a closer look at statistics related to testing challenges, testing processes, and testing tools.
We collected data from different resources, surveys and research, to help tech leaders, managers, manual and automation testers, and all the teams understand the true power of automation testing, the reasons for demand for testing, and how it opens the strategic potential of becoming genuinely agile.
And looking ahead, the most common answer to the need for test automation is to reduce the cost or time spendings on a software release. And while this is just the tip of the iceberg, there are many obvious benefits of choosing automation as companies move from traditional to agile software development approaches.
Testing Challenges
Nowadays test stability and test coverage are the most painful challenges for testing teams. 22% of companies mentioned test stability as the most painful challenge for testing teams, and 20% mentioned test coverage.
As the modern apps and software market is constantly changing, in addition to constant browser and OS updates, maintaining sufficient testing coverage is increasingly difficult. And frequent changes also impact test stability.
On the way to achieving quality at speed, there are two major barriers: frequent requirement changes (reported by 46% of companies) and the lack of time (according to 39% of companies).
To improve the software quality and overcome challenges, testing teams want to implement shift-left testing to reduce the impact of the time-consuming aspects on testing. And right now manual testing is the most time-consuming activity in the testing cycle. 35% of companies mentioned manual testing as the most time-consuming activity within a testing cycle according to these software testing statistics.

Companies are prioritizing moving from manual to automated testing as quickly as possible and that’s why moving to automated testing is the top priority around software testing (30% of companies mentioned it as the top priority according to these software testing statistics).
The main advantage of automated testing over manual testing is that it allows you to conduct more tests in less time. This improves performance and extends testing capabilities.
Although manual testing will always be necessary in certain cases, automation will help testers complete more tasks in less time, improve testing coverage and meet test market requirements.
85% of development managers say that it is becoming harder to deliver innovation faster, without compromising on quality and increasing the risk of bugs in production; 90% say that the automation of a large number of test cases may become the single most important factor in their success, as the pressure on IT increases, requiring accelerated innovation.
Interesting software testing statistics: in many companies other team members also take part in the formal testing process. For example Developers, Product Owners, Support Specialists, End Users may take part in this process. 36% of testers indicated that 10-50% of testing is done by non-dedicated testers.

Testing Processes
Adopting some sort of automated software testing (77% of companies mentioned it among different testing practices) and continuous testing (72%) is growing within the industry. The main primary strategic driver in pursuing a test automation strategy is the desire to improve overall quality (55% of companies indicated it).
For 43% of companies, automation is a key part of their quality assurance process, while for 23% it is new and promising.
More than 24% of companies have automated 50% or more of their test cases; 33% of companies would like to automate between 50% to 75% of their test cases, while 21% are aiming to automate more than 75% of their test cases.
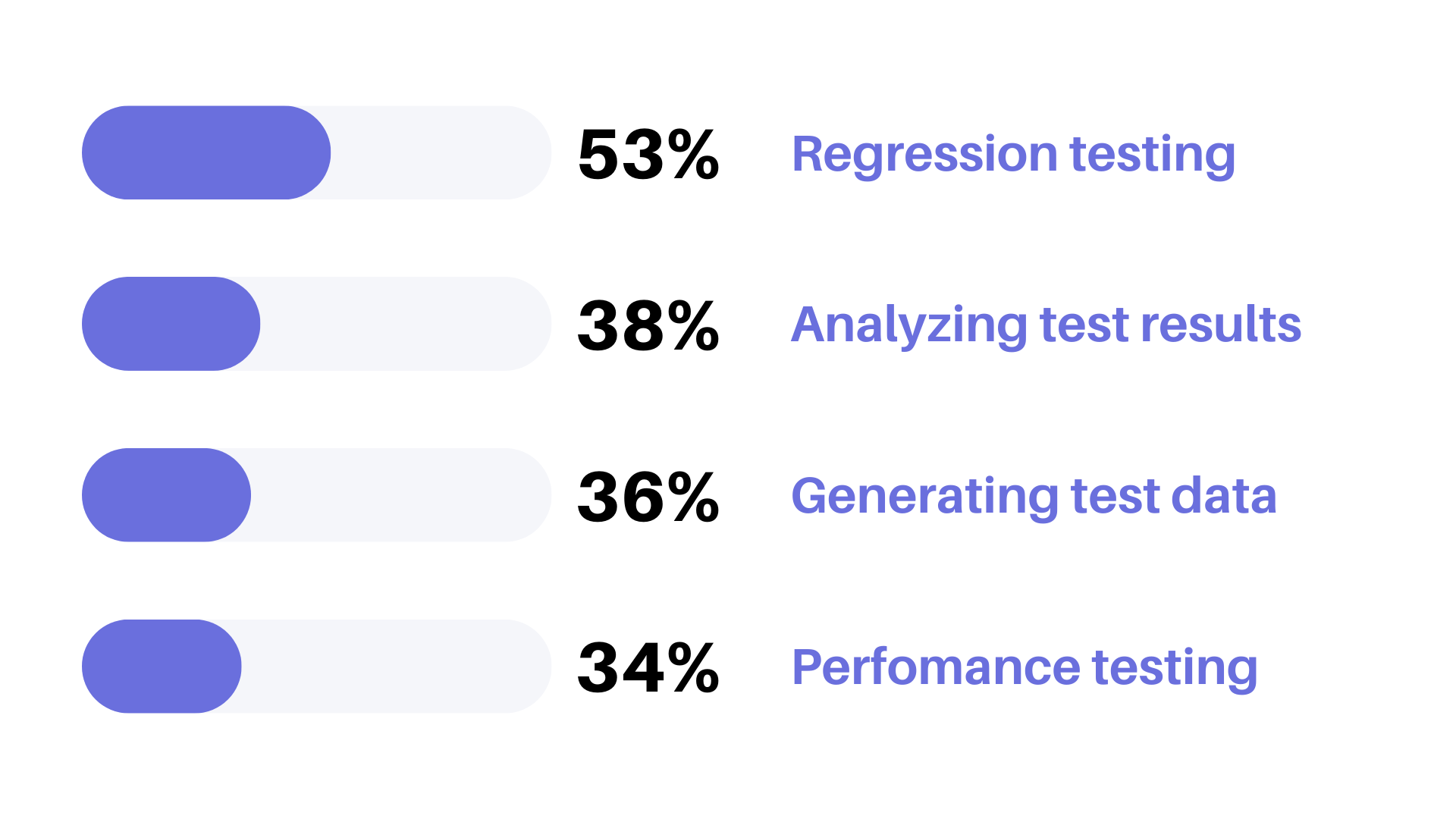
Teams integrated automation into more testing activities. Companies applied automation to regression testing (53% of companies), analyzing test results (38%), generating test data (36%), and running performance tests (34%).
Overall, 73% of testers use scripting and/or test automation for functional and regression testing.
While shift-left testing will remain critical to effective functional testing, shifting more aspects of testing left will be especially important in the next few years.
86% of companies follow Agile or Agile-like principles in the development process.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has great potential for automating testing. Technology can reduce or even eliminate the need for human participation in such time-consuming processes as the development and generation of tests, data preparation, test execution, verification, and maintenance of tests.
Still, less than 50% of companies use some AI capabilities for their test automation. AI is mainly used to create test cases and scenarios, generate test data, detect defects, and prioritize and select tests. This indicates that organizations, especially automation tool vendors, continue to improve the implementation of artificial intelligence for testing automation.
38% of testers indicated themselves as an active part of defining and maintaining the CI/CD process, while the CI/CD process facilitates the process of bringing products to market faster than ever before, and ensuring continuous code delivery to production and a constant stream of new features and bug fixes.
Testing Tools
The interest in test automation tools is on the rise. Fewer QA teams are applying open-source tools. Instead, they employ commercial tools to use their time more efficiently on automated testing.
Selenium is the most widely used tool, but its popularity has declined sharply over the last four years, going from 86% in 2018 to 54% in 2020, and 37% in 2021.
And 39% of companies are interested in using codeless test automation solutions.

Testing teams are keeping up with software testing automation trends to deliver a positive return on investment (ROI): more than 60% of companies received good ROI thanks to automation.
72% of companies indicated that their companies allocate between 10 and 49% of their overall QA budget to test automation related expenditures.
The selection of the tool depends on the Application Under Test (AUT). However, according to these test automation statistics, specialists stress having proper training documents and tutorials for the testing tools (51% of companies mentioned it). Functionality and feature-richness are also one of the top-most concerns (48% of companies mentioned it) for tool selection criteria, while 45% of companies count on the tools’ ability to generate good test reports. A similar number of companies (46%) mentioned the level of programming skills required to operate the tool as a key decision-maker.
The most common challenges in applying test automation tools are the lack of skills and experience in tools and frequently changing requirements.
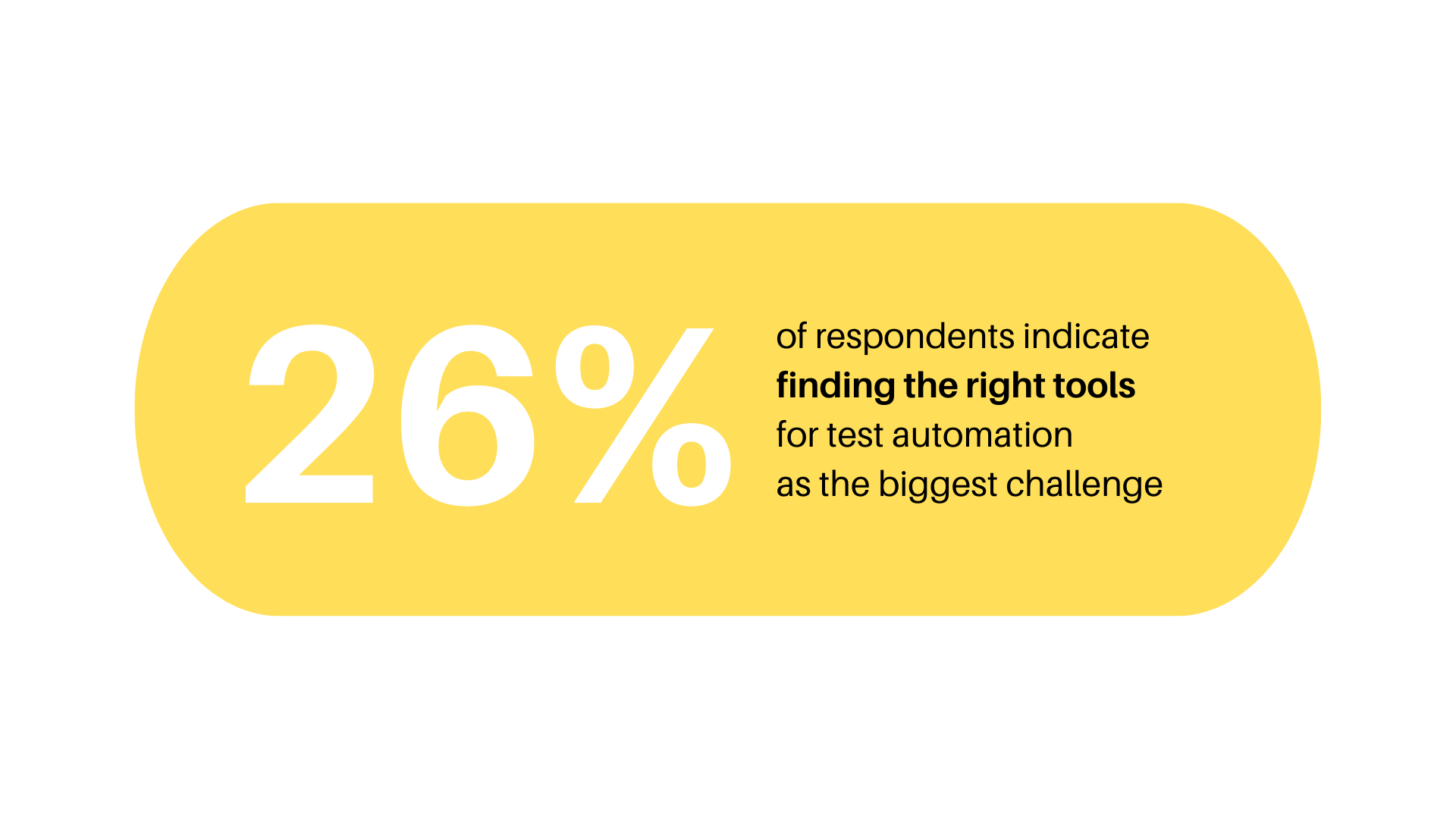
Also 26% of companies indicated finding the right tools for test automation as the biggest challenge that they face.
As for the metrics that best indicate successful test automation implementation, 28% of companies preferred the speed of delivery, and 26% of companies preferred the number of bugs found.
All mentioned challenges are not necessarily essential as automation processes and testing tools have the potential to eliminate the need for advanced skills required for automation and to cope with changing requirements.
It’s worth mentioning that 90% of companies agree or strongly agree that investing in testing transformation is critical to enabling continuous delivery; 45% of companies prioritized partnering with third-party software testing services.
Software Testing Market
In the past few years, the software testing market has witnessed significant changes: test automation has evolved to speed up the time to market for software with the highest testing quality. Automation has always been an eye-catching trend, as it lessens the standard testing efforts and accelerates the testing process.
The automation testing market is expected to grow at 19.2% CAGR from USD 20.7 billion in 2021 to USD 49.9 billion by 2026.
The growth of the automated testing market is driven by the increasing need to implement the transition from manual testing to automated testing.
In turn, the codeless testing market is expected to increase at 15.5% CAGR from USD 1.5 billion in 2021 to USD 6.3 billion by 2026. According to these data, codeless market share in 2023/2022 is expected to be around 6.5%.
Factors responsible for the rapid growth of the codeless testing market include the ease of code evaluation by non-technical team members and the reduction in time that testers spend on repetitive test cases.
Interesting fact
While we were preparing this material, we came across the following software testing statistics: 57% of testers learn testing “Just doing it” 🙂
Conclusion
Automation has become a major activity in the last few years as companies look to accelerate software innovation and sharpen their competitive edge. Automation provides significant benefits and also allows companies to efficiently allocate resources to perform more important tasks that move the business forward.
Therefore, it is not surprising that the above test automation metrics show a growing interest in automating testing, as organizations are looking for a way to simultaneously improve the quality, speed, and efficiency of their efforts to bring innovations to market, without fear that higher speed means lower quality.
If you want to try test automation for your web app or website, you can use DogQ – a codeless test automation tool, which can perform regression, e2e, functional, and other types of web testing.
